CCI Indicator
In this chapter, you will learn –
- What the CCI (Commodity Channel Index) indicator is and its purpose in trading.
- How the CCI indicates overbought and oversold conditions.
- The method of interpreting CCI readings for trading decisions.
- Adjusting CCI settings and the effects of different settings on trading signals.
- Effective strategies for utilizing the CCI in various market conditions.
The CCI Indicator
The Commodity Channel Index (CCI) is recognized as an essential oscillator indicator in the trading world. It plays a significant role in identifying when an asset is overbought – meaning it is bought too much, or oversold – meaning it is sold too much. This indication is crucial for traders as it provides a clear signal about the saturation points of an asset in the market.
Additionally, the CCI helps in pinpointing the peaks and troughs in an asset’s price.
These peaks and troughs are vital indicators, as they can reveal the weakening of an ongoing trend or signal the end of a trend, paving the way for a potential change in the market’s direction. This aspect of the CCI is particularly useful for traders looking to understand the momentum and trend reversals in the market.
Leveraging the information provided by the CCI, you are empowered to make strategic trading decisions.
- The CCI enables you to enter a trade at the very beginning of a trend, maximizing potential gains.
- Conversely, it can alert you to exit a trade before the trend reverses, helping to protect your investment from adverse market movements.
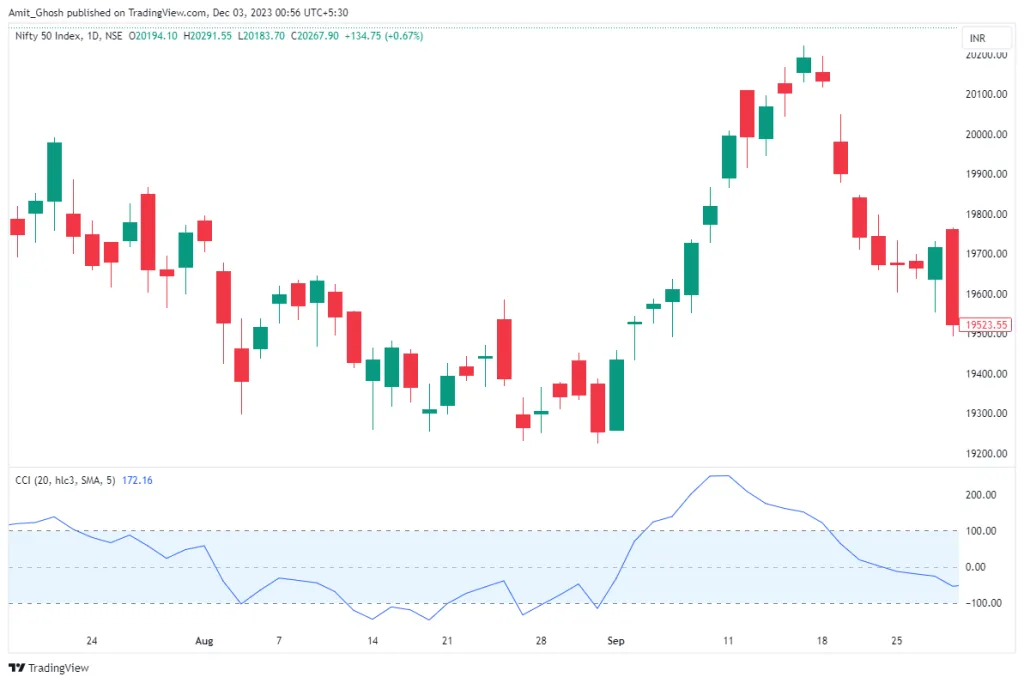
How to trade using CCI Indicator
The representation of the CCI indicator on charts is done using a line akin to a moving average, which aids in smoothing and simplifying the complex market data for better analysis.
The calculation of the CCI generates a value that predominantly stays within a defined channel, typically ranging between +100 and -100, as can be observed in the chart.
- When the CCI reading exceeds +100, it signals that an asset may have been overbought, indicating a potential downward movement in price.
- Conversely, a reading below -100 implies that the asset could be oversold, suggesting an upward price movement might follow.
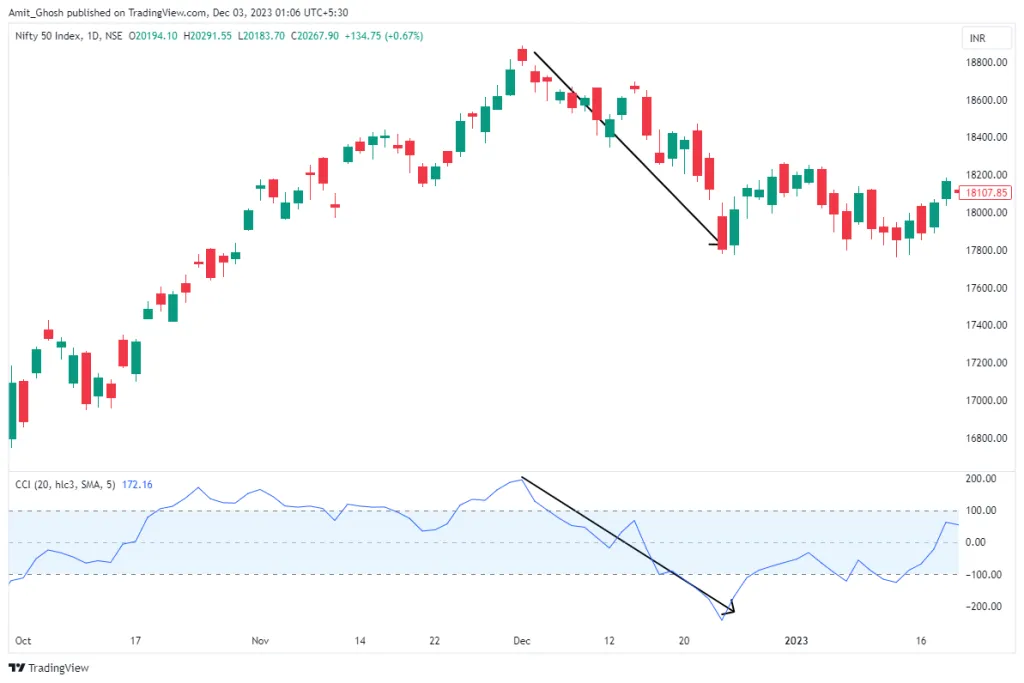
In the displayed image, you’ll notice the price crossing over the +100 mark on the CCI indicator. This movement signifies that the asset is potentially overbought. As the price then crosses back below this threshold, it’s an indication where selling could be considered.
The key points in the image to observe are:
- The moment when the CCI climbs above +100, signaling the overbought condition.
- The specific area where the CCI starts to reverse, moving back below the +100 level.
- The point of potential short entry, where the market begins its reversal following the overbought signal.
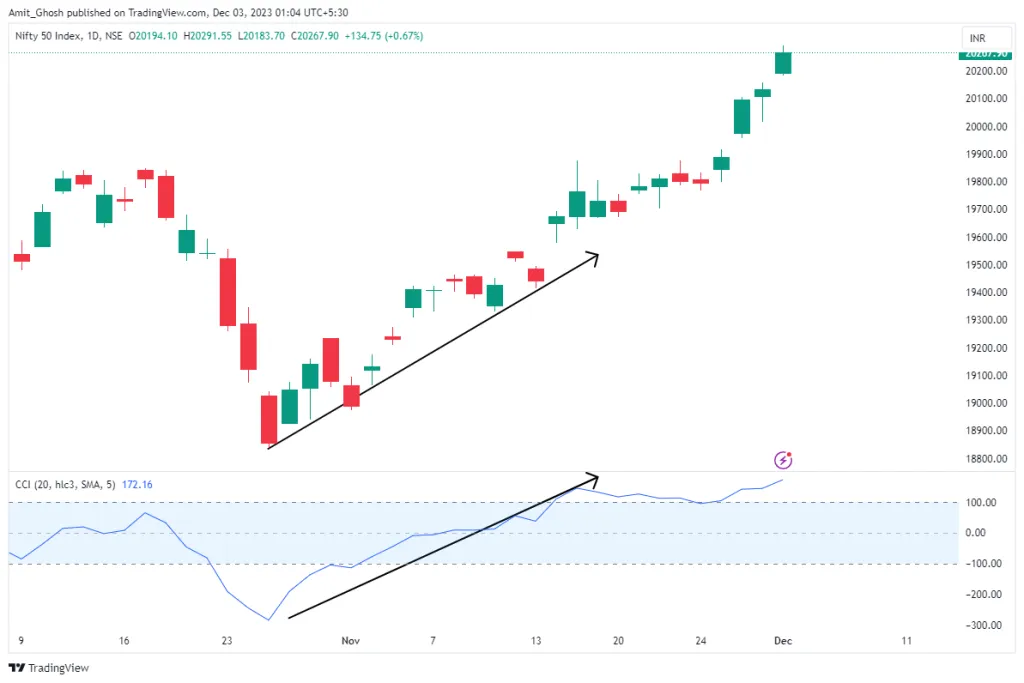
Changing the CCI indicator settings
The default setting for the Commodity Channel Index (CCI) indicator is set at 14. This means the CCI compares the recent price changes of an asset against the average price changes over 14 distinct time periods. However, this setting is adjustable and can be modified according to individual trading strategies and preferences.
Opting for a setting lower than 14 on the CCI makes the indicator more sensitive.
It results in the average line oscillating between the +100 and -100 levels more frequently, indicating quicker reactions to price changes but also not staying within either the overbought or oversold cycle for extended periods. To illustrate the impact of different settings on the CCI, consider the next two images.
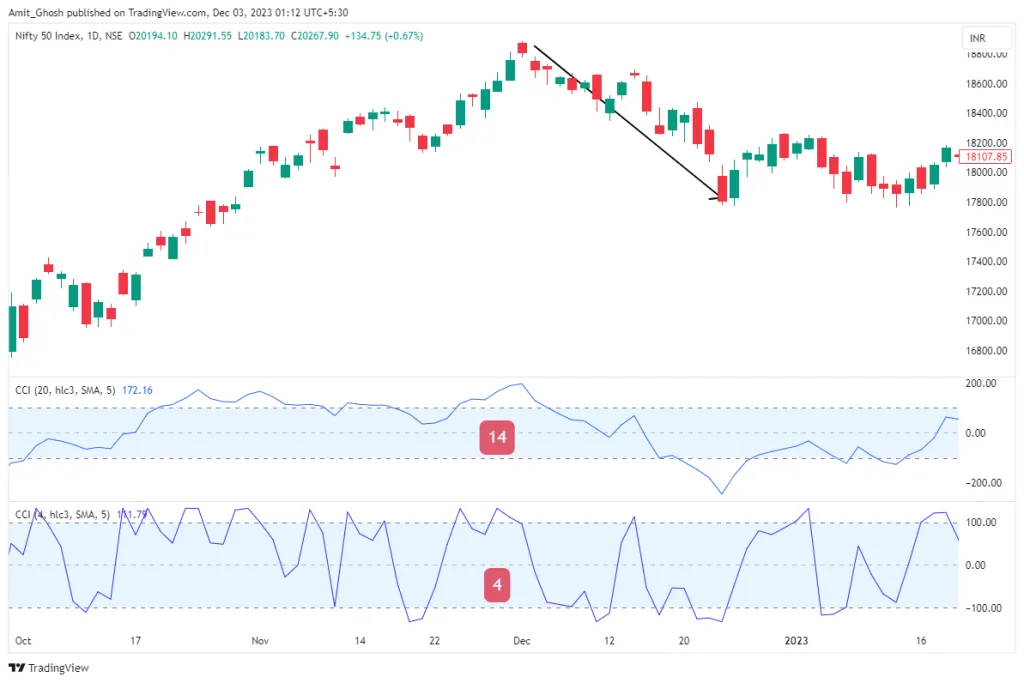
The first image above showcases a CCI with a setting of 4, significantly lower than the standard 14. Observe the frequency with which the average line crosses above and below the +100 and -100 thresholds.
In contrast, the following image displays a CCI set at a much higher value compared to the standard 14.
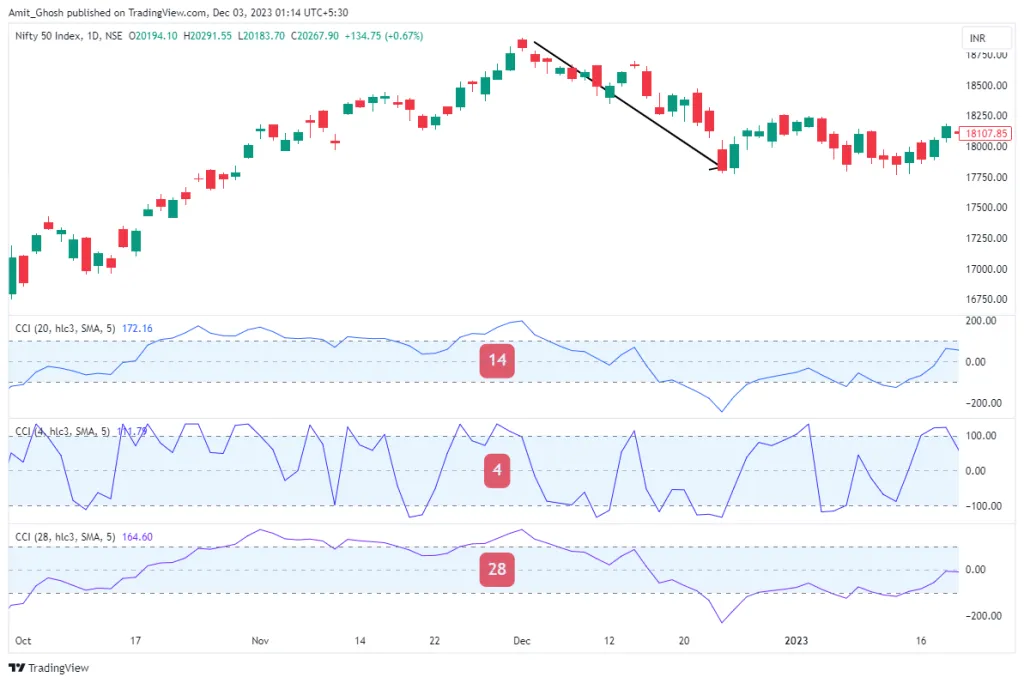
Here, you can see that the average line rarely moves beyond the key +100 and -100 levels and, when it does, tends to remain there for a longer duration.
It’s important to consider the implications of adjusting the CCI settings.
Lower CCI Settings:
- A lower setting may lead to a rapidly changing CCI reading, potentially increasing the number of false signals.
- However, when these signals are accurate, they can allow traders to enter trends earlier, offering greater profit opportunities.
Higher CCI Settings:
- Conversely, a higher CCI setting leads to fewer overall signals.
- This reduction in signal frequency can help minimize false signals but may also decrease the profit potential as it often results in later entries into market trends.
Setting the CCI higher means the indicator changes less frequently, which can be advantageous in maintaining positions for a longer duration, thereby reducing the impact of false signals. However, this approach might delay trade entries, potentially leading to smaller profits as the trend may be well established by the time the signal is given.
When modifying the settings of the CCI, it’s crucial to test whether these changes enhance or detract from the effectiveness of your trading strategy. Continuous testing and adjustment ensure that the CCI settings are optimized for your specific trading needs and market conditions.
Conclusion
- The CCI (Commodity Channel Index) is an oscillating indicator, instrumental in identifying high (peaks) and low (troughs) points in an asset’s price.
- It is useful in signaling the potential end or weakening of a trend, aiding in entering a trade at the beginning of a trend or exiting before the trend turns against you.
- On charts, the CCI is represented using a line similar to a moving average, providing a clear visual interpretation.
- The CCI typically operates within a range, usually fluctuating between +100 and -100, helping in understanding market conditions.
- A CCI value above +100 suggests an overbought condition, indicating a potential selling point. Conversely, a value below -100 implies an oversold condition, signaling a buying opportunity.
- The CCI is versatile and can be applied across various time frames in trading.
- Its standard setting is at 14, balancing recent and average price changes over 14 periods. However, this setting can be adjusted.
- A lower setting (less than 14) makes the CCI more sensitive, causing it to oscillate between +100 and -100 more frequently but not staying in those zones for long.
- A higher setting (more than 14) results in a less sensitive CCI, which reaches or exceeds the +100 and -100 levels less often but remains there longer.
- A very low setting may lead to early trend detection but also a higher chance of false signals, while a very high setting can reduce false signals but may limit profit potential.
- It’s crucial to test any changes to the CCI settings, ensuring they actually enhance your trading strategy and results.